Key Findings
The 11th edition of Knocking at the College Door: Projections of High School Graduates highlights key findings by WICHE experts about the changing student demographics facing the U.S. education systems at the K-12 and postsecondary levels. Explore projections about the total number of high school graduates, the race and ethnicity breakdown of these student populations, and data profiles of each state, region, and nation. This edition also analyzes the impact of the COVID-19 global pandemic on students now and for years to come.
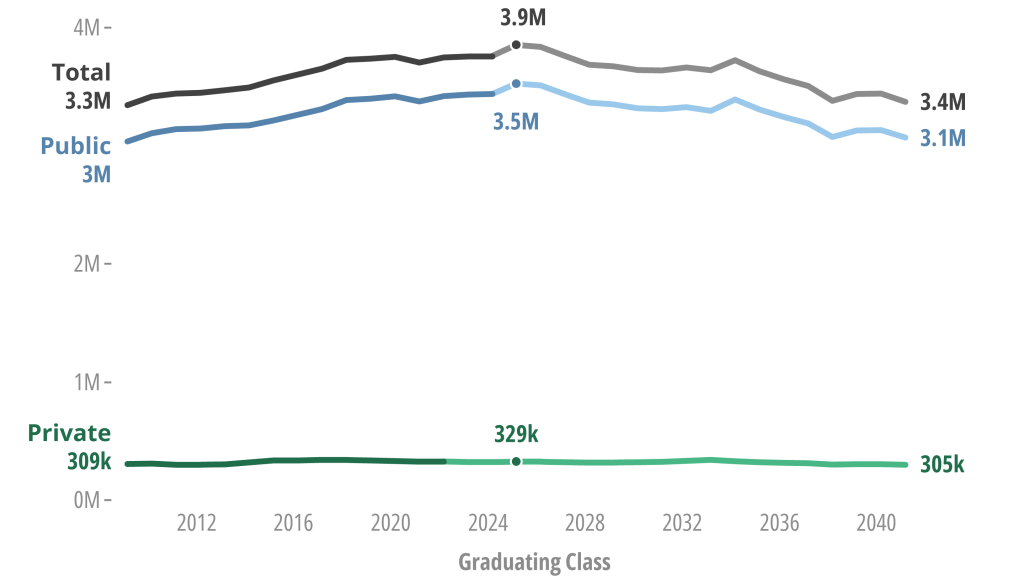
The total number of high school graduates is expected to peak in 2025, then decline through 2041.
WICHE projects that the total number of high school graduates will peak in 2025 before entering a period of steady decline through 2041 attributable to fewer births 18 years prior (when birth rates fell more sharply due to the Great Recession). Ultimately, the nation is projected to see a 13% decline from the peak through the end of the projections.
Although our analysis focuses primarily on the number of high school graduates, it is important to recognize that K-12 systems have already been grappling with this peak and subsequent decline as lower enrollments have made their way through earlier grades.
This broad and substantial decline is primarily dependent on two key factors: the number of births in previous years and the rate at which students progress through school and earn a high school diploma (including high school graduation rates). Other factors like net migration and mortality also contribute to the total number of high school graduates. Although our analysis focuses primarily on the number of high school graduates, it is important to recognize that K-12 systems have already been grappling with this peak and subsequent decline as lower enrollments have made their way through earlier grades.
High school graduates, reported (2009 to 2023) and projected (2024 to 2041)
To see a data visualization of this key finding, click here.

 This work is licensed under a
This work is licensed under a